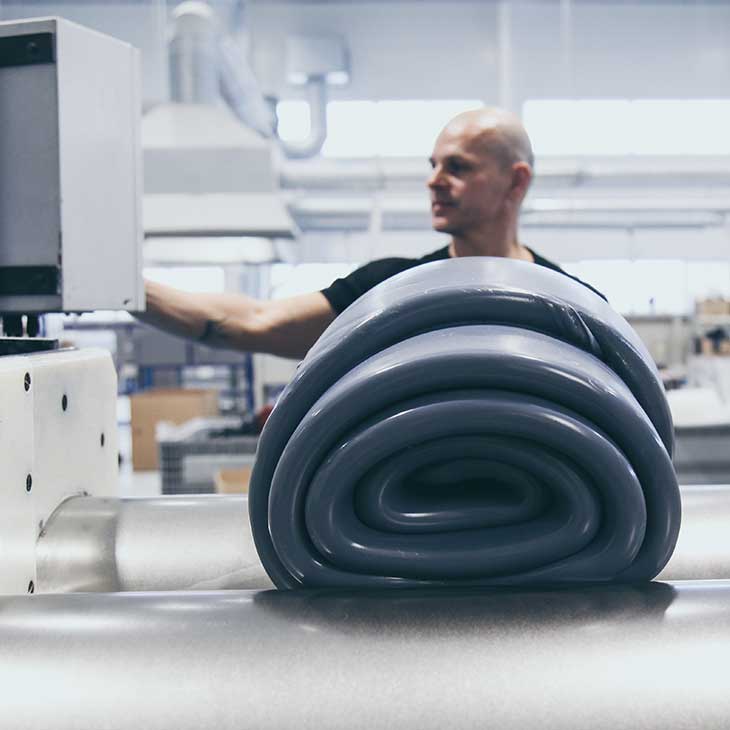
Silicone
SILICONE
For production of silicone, we use the best materials available on the market. We cooperate with recognized and proven manufacturers, such as: Wacker Chemie, Dow Corning, Elkem Silicones, Shin-Etsu Chemical.
GENERAL PROPERTIES OF SILICONE
Structure of the HTV silicone rubber is similar to glass or quartz because it is a combination of silicon and oxygen. However, its structure differs from other rubbers because the properties of products made from such rubber differ significantly from properties of other rubber products. In general, they are very resistant to high temperatures while maintaining flexibility at very low temperatures. Their good mechanical and electrical properties remain almost constant in a wide range of temperatures. They withstand exposure to oxygen, ozone, weather conditions, including cosmic rays and UV radiation. Silicone products are known for their very good insulating properties. Many of them are physiologically neutral, surpassing all other currently available elastomers.
OUR OFFER INCLUDES:
- General purpose silicone (crosslinked with peroxides)
- Platinum-crosslinked silicone
- High tear resistance silicone
- Conductive and anti-static silicone (with hardness from 10 to 80°ShA)
- High temperature resistant silicone (+230 / +250 / +300 °C)
- PVMQ low temperature resistant silicone (-110 °C)
- Fluorosilicone rubber – FVMQ
- Low-smoke low-toxicity fire-retardant silicone
- Antibacterial silicone
- Oil-resistant silicone
- Water-vapour-proof silicone
- Silicone with magnetic properties
- Silicone detected by metal detectors and X-Ray
- Silicone resistant to animal and vegetable oils and fats
THERMAL STABILITY
Silicone vulcanizates withstand continuous exposure to hot air at 180°C, and even at 250°C they remain flexible for several thousand hours. They also withstand short-term exposure to temperatures of 300-400°C and higher.
FLAMMABILITY PROPERTIES
The flash point of typical silicone vulcanizates measured in accordance with ASTM-D 1929-68 is approximately 430°C, and the combustion temperature is approximately 750°C. During the combustion of silicone rubber, insulating silica layer is created. As a result, even after a fire, the silicone rubber insulation continues to perform its function for certain amount of time.
FLEXIBILITY IN LOW TEMPERATURES
Silicone vulcanizates generally do not harden and do not disintegrate to a temperature of -55°C. Vulcanizates with a hardness of 50°-60° Shore A can withstand even lower temperatures and show the best flexibility. Silicone rubbers can be used in low, as well as high temperatures without any change in their properties.
GAS AND LIQUID PERMABILITY
Some physical properties result from the molecular structure of silicone rubber. Compared to other elastomers, silicone vulcanizates present high gas and liquid permeability. Their permeability depends on operating conditions such as temperature, pressure difference, etc. In general, the permeability of silicone rubber is about 100 times greater than butyl rubber (having the lowest permeability).
SURFACE PROPERTIES
A useful property of silicone is the inertness of the surface of its vulcanizates, which is strongly anti-adhesive and hydrophobic. On the other hand, silicone rubber can be vulcanized with metals and glass fibres providing very strong joints.
DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES
Dielectric properties of silicone vulcanizates at room temperature are comparable to the best known insulating materials, but silicone rubber clearly outperforms other materials at higher temperatures (up to 180°C) where many of them are useless. Very good dielectric properties of silicones are supplemented by excellent resistance to electric arc.
Colors
Our silicone products can be used in a very wide range of applications. On the Customer’s request, we can dye products in a wide range of colours (RAL).
RAL color palette | |
|---|---|
| 1021 | |
| 3000 | |
| 3013 | |
| 4001 | |
| 5010 | |
| 5015 | |
| 6017 | |
| 7040 | |
| 8015 | |
| 9010 | |
| 9005 | |
| 9017 | |
| 9006 |
Quality Control
The highest quality is guaranteed not only by our raw materials, but also by the quality control during the production process.
Contact with Food (in accordance with the European Union requirements)
Regulation (EC) No. 1935/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 October 2004 on materials and articles intended to come into contact with food and repealing Directives 80/590/EEC and 89/109/EEC (OJ L 338/4 of 13 November 2004)
Commission Regulation (EC) No. 2023/2006 of 22 December 2006 on good manufacturing practice for materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (OJ L. 384/75 of 29 December 2006)
| Poland PZH | Germany BfR XV | USA “Rubber Articles Intended for Repeated Use”, FDA – Code of Federal Regulation, §177.2600 |

